Demonstration page
The structure and functions of the cell
Cell is a integrated system in which distinguish shell cytoplasm and the nucleus. The shell of plant cells consists of cellulose. Depending on the function performed by the cell, the shell may be subject to lignification, suberization, mineralization kutinisation. It is riddled by pores through which goes strands of cytoplasm – plasmodesma that connect the cells together. The shell is formed in the result the cytoplasmic organelles actionin basically by Golgi complex. In the living organisms cells usually do not have a shell, or it has a different structure.
The cytoplasm consists of the plasmalemm, hyaloplasm, organelles and inclusions.
Plasmalemm (elementary biological membrane) comprises three layers: an external and internal - protein and located between them the lipid layer, with two rows of phospholipid molecules (Figure: Cells have complex surfaces, by Raven & Johnson). Protein layers can interlock and form a special hydrophilic pores through which water-soluble substance as ions. Non-soluble complex molecules of protein, vitamins, lipids penetrate special enzymatic membrane pores. This is done as follows: enzymes synthesized embedded in the cell membrane and bind in the cytoplasm and is performed only needed substances.
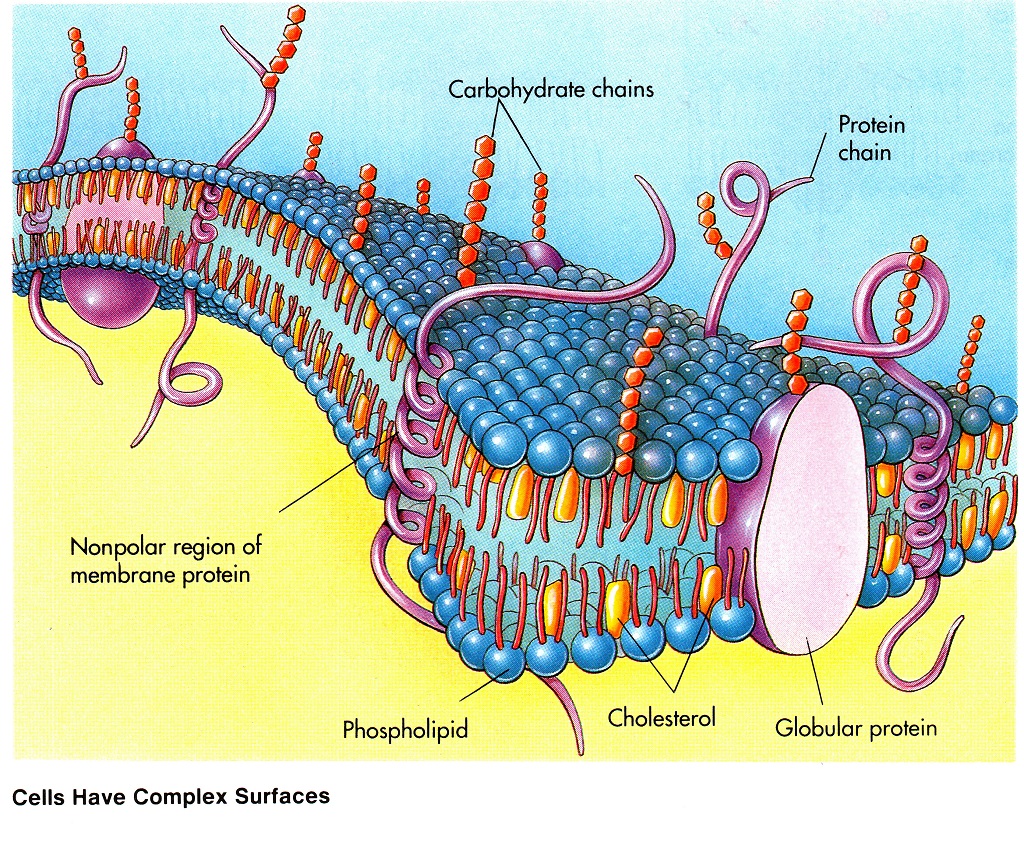
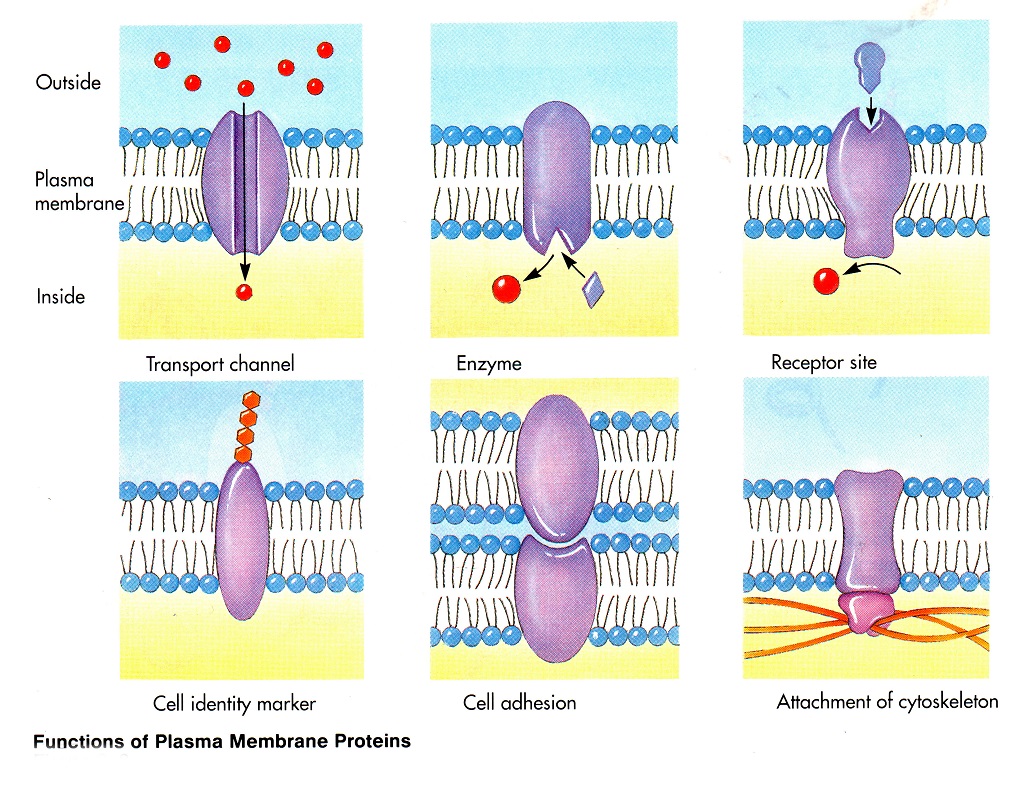
Plasmalemm has a wavy, folded superficiality, which increases the area of its suction. She makes several important functions: regulate metabolism and energy between the cell and the outside world perceives and converts external signals (chemical, sound, mechanical and so on), carries the uptake of solid foreign particles (phagocytosis) and liquid droplets (pinocytosis) (Figure: Functions of plasma membrane proteins, by Raven & Johnson).
Hyaloplasm - heterogeneous colloidal solution that provides the interconnectedness of all cell organelles and processes of its life. Colloidal hyaloplasm characterized by two states: liquefied - sol dense - gel, and may be sol - gel transitions depending on the conditions of life. Hyaloplasm provides cell viscosity elastics, contractility, internal movement. Microtubules and microfilaments - specific protein structures that perform a supporting function of the cell are situated in it. For example: microtubules is main components of flagellum - organoid with special movement function.